
SNP’s polyurethane dispersions (PUDs) contain a complete range of 1K water based aliphatic polyurethane products, which can be used in many different industries and applications. Send us an email or call to start a conversation about working with us.
With this balance of properties, PUDs are key components of coatings for wood, metal, concrete, and plastic. PUDs can be blended with acrylic and styrene butadiene latex to cost-effectively create higher performance coatings. SNP works as a team with the customer to determine the best product within the series to meet the desired properties and application needs. Learn more about our aqueous polyurethanes below.
Polyurethane polymers are made by combining isocyanates (R-N=C=O) with polyols containing hydroxyl (- OH) functional groups. The reaction forms urethane linkages as seen below.
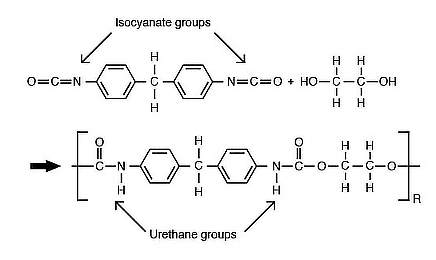
There are two classes of polyurethane dispersions: aromatic and aliphatic. Since the film color stability of aromatic dispersions is suspect, SNP polyurethanes are all aliphatic. These dispersions give clear, heat/UV stable films.
The functionality of the actual polymer is dependent upon the polyol and isocyanate used. By varying these, the characteristics of the resulting polyurethane can be changed. Three polyols are typically used in synthesizing SNP polyurethane dispersions for industrial coatings applications: polyether, polyester, and polycarbonate. Regarding the properties of durability and toughness, these are in ascending order of performance.
The use of co-solvent is typical in PUDs. N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) is a traditional co-solvent; but one that has fallen out of favor with many users. SNP offers co-solvent free and NMP-free products to address the VOC requirements of modern users. Co-solvent free products offer the customer the option to compound without co-solvent or to use the co-solvent of their choice.
SNP 1K PUDs are designed to be used without addition of an external crosslinker. However, if one is needed to meet specific end use properties, SNP has expertise in the proper crosslinking systems to be used with its products. Water based polyurethanes are unique as they have great flexibility and outstanding hardness, which result in a very tough, durable coating. Unlike many polymeric materials, flexibility is maintained regardless of film hardness. Another thing that distinguishes polyurethanes is that they maintain flexibility across a wide range of temperatures.
These materials are often used to replace or supplement the performance of synthetic latex in coatings applications. Typical synthetic latex has difficulty achieving high tensile strength and good flexibility at the same time. Polyurethane dispersions have been shown to build strength, flexibility, durability, chemical, and water resistance into compounded coatings. This is particularly effective in improving the performance of elastomerics for roofing, caulks, and adhesives.
Ask us about ways we may be able to help you address your product/process issues, develop your new products, and/or meet your custom needs.
Copyright © 2025 SNP, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy
Digital Marketing and Website Design by KNOW YOUR WORTH MEDIA