
We have extensive experience testing a wide variety of polymers, plastics, pseudo plastics and composites. Our rheologists can reengineer and reformulate your materials to improve their rheological performance. At SNP Inc., we value our client relationships and work hard to be a beneficial partner in their research endeavors. All work is strictly confidential, and we are fully prepared to perform your rheological tests under a signed confidentiality agreement. Send us an email or call to start a conversation about working with us.
All materials start with an original form at rest that resists flow when an applied shear force is applied. This resistance is due to internal forces that result from interactions between material components. Viscosity is the measurement of this resistance to flow and is a core concept of rheology.
The figure shown illustrates the parameters of the viscosity term and provides the calculation used to obtain its value.
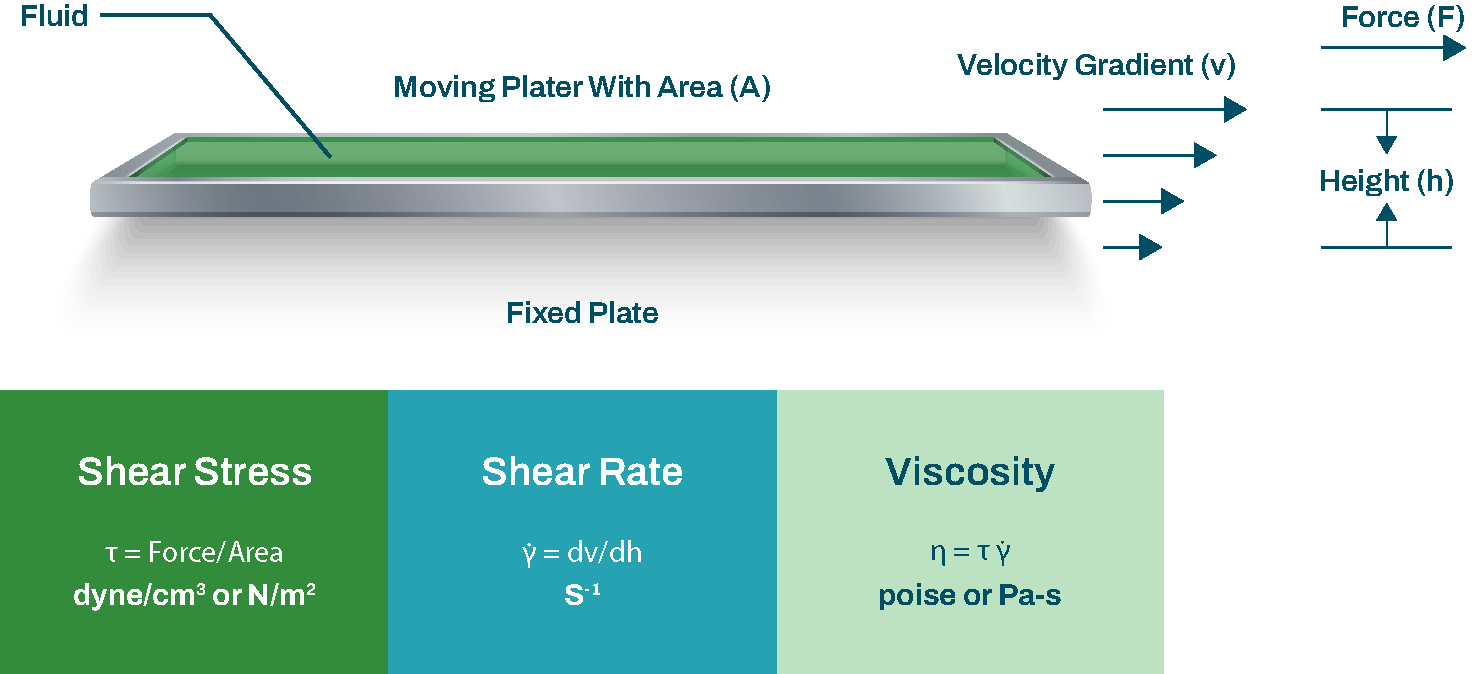
The rheological behavior of materials can be described as either elastic or viscous in nature.
Elastic describes materials that are ridged or solid-like in their behavior. This means that when a stress is applied, the internal forces remain intact, so the energy applied is stored and when it is released the structure completely recovers to its original form.
Viscous describes materials that are fluid-like. This means that when stress is applied, the material readily flows due to the lack of internal forces being present to resist flow. So, for these materials, viscosity is independent of shear rate. All energy put into the system is dissipated as heat and is lost. An ideal Newtonian liquid, such as water, is a good example of a viscous material.
Most polymers, synthetic or natural, will exhibit both viscous and elastic properties and are best described as being viscoelastic. The viscous and elastic contribution of materials depends upon the type and strength of internal structures present. Therefore, the rheological response of a viscoelastic material to shear depends on the stresses applied, the duration of deformation, and physical conditions under which they are applied. This is especially true when the coating is applied using roll, brush, spray, jet and fountain applicators.
When applying a coating to a surface, a shear force is always applied in some form, which subsequently deforms the coating. The applied force can be in the form of shear from a brush or roller during painting or blade or rod on a paper machine coater. Regardless of the application or metering process, immediate coating recovery is essential for uniform film formation.
Ideal coatings are shear-thinning for easy application, recover quickly to prevent patterning, and maintain coating structure to prevent settling of the product during shipment and storage. Most water-borne coatings will use either a synthetic or natural rheology modifier to achieve this balance of good coating performance and storage stability.
Rheology is the study and characterization of the flow of materials. Most people think of fluids in terms of viscosity but some fluids are viscoelastic. Viscoelastic materials exhibit both viscous and elastic behavior when experiencing deformation.
Whenever elastic materials are placed under stress, the strain is exhibited instantaneously as is the recovery when the stress is removed. Because viscoelastic materials have both elastic and viscous properties they exhibit time dependent strain. By analyzing both the fluid and elastic properties of a material, we can predict the reaction of these materials when subjected to these external forces. While some materials will flow when subjected to force, others will resist or will experience deformation then recovery.
Rotational viscometers operate under only one measurable flow condition and relate the torque required to turn an object in a fluid at a known speed to the viscosity of that fluid. The relationship is based on the fluid remaining stationary as an object moves through it, or the object is stationary as the fluid moves past it with the resultant drag caused by relative motion of the fluid and a surface is a measure of the viscosity.

The Hercules Hi-Shear Viscometer system measures the flow properties of dispersions and coatings subjected to varying degrees of shear. The Hercules Hi-Shear Viscometer produces continuous results reflecting sample reaction to dynamic shear conditions over time. The shape of the rheogram produced from the Hercules Viscometer can be used to predict flow performance of a material based on changes in shear rate.

A rheometer is used to measure fluid flow response to applied forces. A rheometer is used when fluids cannot be defined by a single value of viscosity therefore requiring multiple parameters to be defined and measured.

Ask us about ways we may be able to help you address your product/process issues, develop your new products, and/or meet your custom needs.
Copyright © 2025 SNP, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy
Digital Marketing and Website Design by KNOW YOUR WORTH MEDIA